Are you confused about whether forced air heaters and air handlers are the same thing? You’re not alone.
Many homeowners struggle to understand these terms, even though they play a big role in how your home stays warm and comfortable. Knowing the difference can save you money, improve your heating system’s efficiency, and help you make smarter choices for your home.
Keep reading to clear up the confusion and discover exactly what each one does for your space.
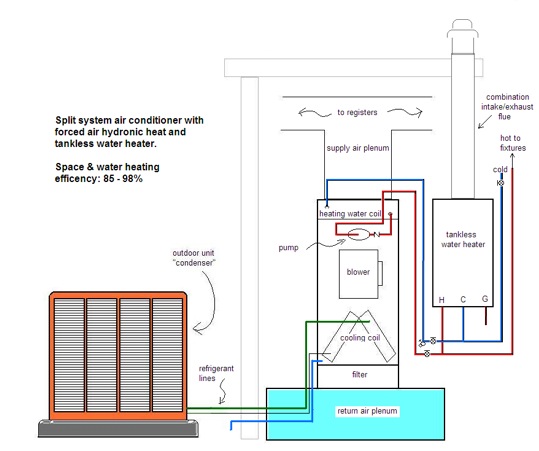
Credit: www.totalplumbingfl.com
Forced Air Heaters Basics
Forced air heaters are common in many homes and buildings. They use air to spread warmth quickly. Understanding their basics helps you see how they differ from other heating systems. These heaters rely on a fan or blower to push warm air through ducts. The warm air moves into rooms fast, making spaces comfortable in cold weather.
How Forced Air Heaters Work
Forced air heaters heat air using a burner or electric element. A fan then pushes the warm air through ducts. The air flows out of vents into rooms. Cooler air returns to the heater through return vents. This cycle repeats to keep the space warm.
Common Types Of Forced Air Heaters
There are several types of forced air heaters. Gas furnaces burn natural gas to create heat. Electric furnaces use electric coils to warm the air. Oil furnaces burn oil for heat. Heat pumps can also work as forced air heaters in mild climates.
Benefits Of Forced Air Heating
Forced air heating warms rooms quickly and evenly. It can also work with air conditioning systems. This allows for year-round comfort using the same ducts. Filters in the system help clean the air. Maintenance is simple and parts are easy to find.
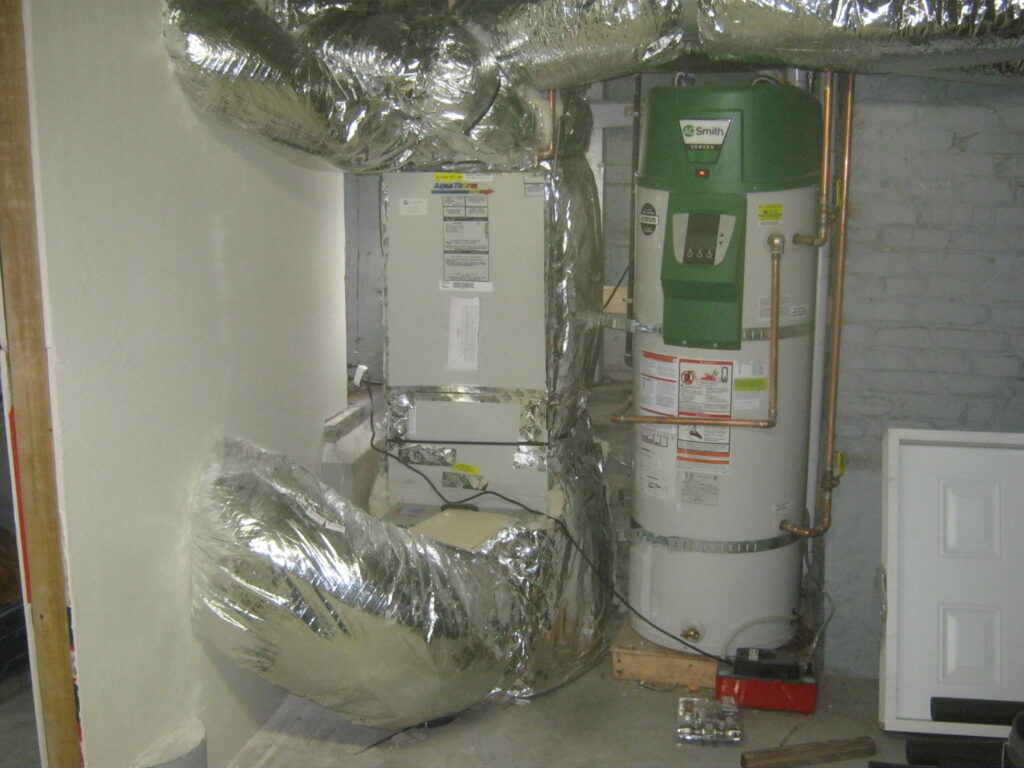
Air Handlers Explained
Air handlers are key parts of many heating and cooling systems. They move air through your home or building. The air can be warm or cool, depending on the system.
Understanding air handlers helps you know how your HVAC works. It also shows how they differ from forced air heaters.
Role Of Air Handlers In Hvac
An air handler moves air through ducts. It pushes warm or cool air into rooms. It works with heating and cooling units.
Air handlers keep air circulating. This helps keep the temperature steady. Without them, air would not flow properly.
Components Inside An Air Handler
Inside an air handler are several parts. A blower fan moves the air. Filters clean the air before it moves.
There is also a coil. This coil heats or cools the air. Controls and dampers help manage airflow.
Functions Beyond Heating
Air handlers do more than just heat air. They also cool and filter air. They help improve indoor air quality.
Some models add moisture to the air. Others remove excess moisture. This keeps your home comfortable year-round.
Key Differences Between Forced Air Heaters And Air Handlers
Understanding the differences between forced air heaters and air handlers helps in choosing the right system. Both play roles in heating and cooling, yet they work differently. Knowing their key differences can improve comfort and efficiency in your home.
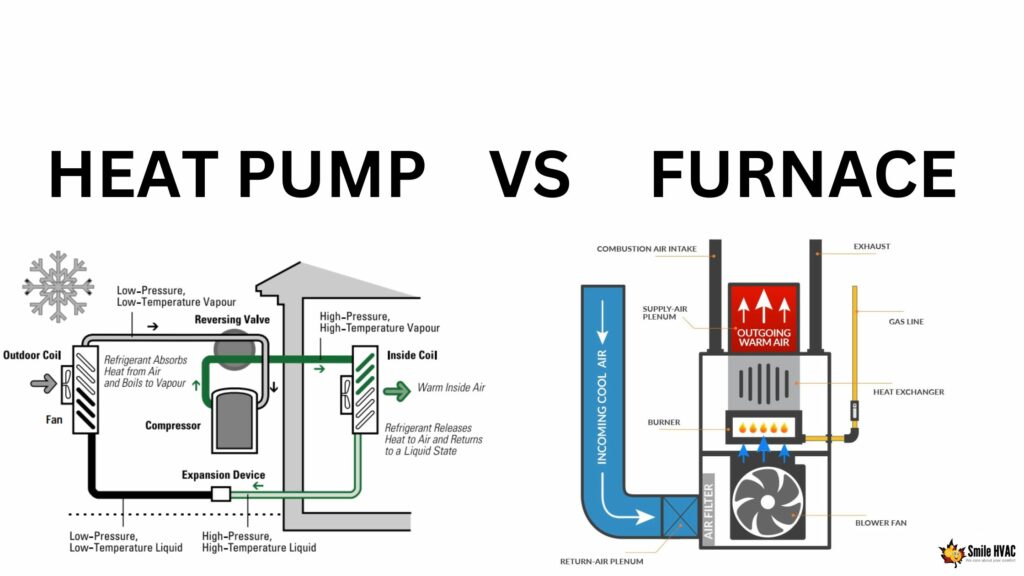
Heating Mechanism
Forced air heaters use a heat source like gas or electricity. They warm the air directly before sending it into your rooms. Air handlers do not create heat themselves. They move air over a separate heating or cooling element.
System Integration
Forced air heaters often work alone or with simple controls. Air handlers are part of larger HVAC systems. They connect to heat pumps or furnaces to manage air flow throughout the house.
Air Distribution Methods
Forced air heaters push heated air through ducts to warm spaces quickly. Air handlers circulate air continuously, allowing for better air mixing. This helps maintain steady temperatures and improves indoor air quality.

Credit: ecoperformancebuilders.com
Energy Efficiency And Performance
Energy efficiency and performance are key factors to consider for heating systems. Both forced air heaters and air handlers serve to warm your space, but they do this differently. Understanding their energy use and maintenance helps you choose the right option. Performance also depends on how well the system holds up over time. These points affect your comfort and energy bills.
Comparing Energy Use
Forced air heaters use fuel or electricity to create heat directly. This process can consume more energy because it heats the air quickly. Air handlers do not produce heat themselves. They work with heat pumps or furnaces to move warm air. This can save energy by using existing heat more efficiently. Overall, air handlers often offer lower energy use in mild climates.
Maintenance Requirements
Forced air heaters need regular checks for safety and function. Filters must be cleaned or replaced often to keep airflow steady. Air handlers also require filter care but less attention to the heating parts. Cleaning the blower and checking the coils ensure good performance. Both systems need some upkeep, but forced air heaters may need more frequent service.
Longevity And Durability
Forced air heaters face more wear because they generate heat directly. Parts like burners or heating elements may wear out faster. Air handlers usually last longer since they move air without producing heat. Their parts face less stress and have fewer chances of failure. Choosing a durable system means fewer repairs and longer comfort.
Choosing The Right System
Choosing the right heating system affects your home’s comfort and energy use. Understanding the differences between forced air heaters and air handlers helps make a smart choice. Each system suits different needs and situations. Consider key factors before deciding. This section guides you through those points to find the best fit for your home.
Factors To Consider
Think about your home’s size and layout. Large spaces need powerful systems. Small homes might work with simpler units. Check existing ductwork to see if it matches the new system. Energy efficiency matters for long-term savings. Noise levels can affect comfort too. Also, consider how often you use heating. These details shape which system works best.
Matching Systems To Home Needs
Forced air heaters warm air directly. They work well in homes needing quick heat. Air handlers move air through ducts and can connect to heat pumps. They suit homes needing both heating and cooling. Look at climate and your personal comfort needs. Some homes need heating only. Others want flexible temperature control year-round.
Cost Implications
Initial purchase price varies between systems. Forced air heaters usually cost less upfront. Air handlers may need extra equipment, raising costs. Installation complexity affects labor charges. Operating costs depend on energy use and efficiency. Maintenance expenses also differ. Balance upfront costs with long-term savings. Choose a system that fits your budget and comfort.
Credit: dpsjanowicewielkie.pl
Common Misconceptions
Many people mix up forced air heaters and air handlers. This confusion comes from how similar they seem. Both deal with air and heating, but they are not the same. Clearing up these misunderstandings helps you know which one fits your needs.
Terminology Confusion
The names forced air heater and air handler sound alike. It makes people think they are the same device. Forced air heater means a unit that heats air and pushes it into rooms. Air handler means a machine that moves air but may not heat it. The difference lies in their main job.
Function Overlaps
Both systems move air through your home. Sometimes, an air handler has a heating part inside. This overlap causes confusion. Forced air heaters always heat air before sending it out. Air handlers may only circulate air without heating it. Knowing this helps you understand their true roles.
Installation Myths
Some believe forced air heaters and air handlers are installed the same way. This is not true. Forced air heaters need fuel or electric connections for heat. Air handlers link to the heating or cooling system and focus on airflow. Proper installation depends on which system you have.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Main Difference Between Forced Air Heaters And Air Handlers?
Forced air heaters produce heat using fuel or electricity. Air handlers only move air and do not create heat.
Can Air Handlers Work Without Forced Air Heaters?
Yes, air handlers can circulate air for cooling or ventilation without heating. They work with AC units or heat pumps.
Do Forced Air Heaters Include Air Handler Components?
Forced air heaters often have built-in blowers similar to air handlers. But their primary job is heating, not just air movement.
Which System Is Better For Home Heating, Heater Or Air Handler?
Forced air heaters are better for heating homes directly. Air handlers depend on external heat sources to warm air.
How Do Forced Air Heaters And Air Handlers Affect Energy Use?
Forced air heaters use energy to generate heat. Air handlers use less energy as they only move air.
Can Air Handlers Improve Indoor Air Quality?
Yes, air handlers can include filters to clean the air. This helps remove dust and allergens from your home.
Conclusion
Forced air heaters and air handlers serve different roles in home comfort. One heats the air directly, while the other moves air through your system. Knowing their differences helps you choose the right option. Both work together in many homes for efficient heating and cooling.
Understanding these basics can save money and improve comfort. Keep these points in mind when deciding on your heating system. It makes your home warmer and energy use smarter. Simple knowledge goes a long way.
